RAT HOLE MINING
It is a well known fact that 15 miners are stuck in a Rat Hole Mine in the Meghalya State of India since December 13 of 2018.
A news Article is now flashing that Indian Navy found the Dead Body of one of the miner in the search operation . It is hard to guess what happed with the remaining 14 miners and clear picture will only emerge after any official statement f the operation search team.
The official Confirmation of Indian Navy regarding the body of miner is as follows :-
#MeghalayaMineTragedy #Flash One body detected by Indian Navy Divers using Underwater ROV at a depth of approx 60 feet and 210 feet inside a rat-hole mine @SpokespersonMoD @DefenceMinIndia @nsitharaman @PMOIndia pic.twitter.com/sP1sv6ikRn— SpokespersonNavy (@indiannavy) January 17, 2019
#MeghalayaMineTragedy The depth is 160 feet (and not 60 feet) and the body has been pulled upto the mouth of Rat-hole mine and shall be extracted out of the mine under the supervision of Doctors— SpokespersonNavy (@indiannavy) January 17, 2019
So What is meant By Rat Hole Mine :-
⇨ Rat Hole Mines are Horizontal tunnels, around 3 to 4 Feet high with longitudinal spread of as high as 160 feet. The one in news is estimated of 160 ft length. Even holes as long as 300 ft have also been noticed by Journalist in the Meghalya. Workers need to crawl in such mines for extracting coal. These Pits are called small scale mines and operates beyond the scope of Coal Mines Nationalisation Act.
⇨ So What actually happened ? 15 workers were mining in one such mine situated in East Jaintia Hills of Meghalya. The water from the adjacent 'Lytein' river gushed in to the mine and thus entrapping the miners in to the mine itself.
⇨ They are basically illegal, un-monitored mines and coal is extracted by workers using pick axes. It is estimated that annually around 5 metric tonnes of coal is extracted from such mines. Practice is in general unique to Meghalya. Coal output of these mines are even used by industries in the state.
⇨ Illegal mines also causes major problems to the surrounding environment and it is said that such mining activities destroy the environment, pollute the water and kill the fish etc.
⇨ National Green Tribunal had put a blanket ban on Coal mining Activities in Meghalya around four years ago. A step taken in a right spirit has unfortunately helped in the increase of the ill legal mining activities in Mehalaya. It is estimated that mining activities prior to this ban were giving the state a revenue of around 700 Crore.
⇨ Several activist opposing the idea of Rat Hole Mines have been severely injured allegedly by Mine Mafia in recent past.
⇨ Rat Hole Mines are Horizontal tunnels, around 3 to 4 Feet high with longitudinal spread of as high as 160 feet. The one in news is estimated of 160 ft length. Even holes as long as 300 ft have also been noticed by Journalist in the Meghalya. Workers need to crawl in such mines for extracting coal. These Pits are called small scale mines and operates beyond the scope of Coal Mines Nationalisation Act.
⇨ So What actually happened ? 15 workers were mining in one such mine situated in East Jaintia Hills of Meghalya. The water from the adjacent 'Lytein' river gushed in to the mine and thus entrapping the miners in to the mine itself.
⇨ They are basically illegal, un-monitored mines and coal is extracted by workers using pick axes. It is estimated that annually around 5 metric tonnes of coal is extracted from such mines. Practice is in general unique to Meghalya. Coal output of these mines are even used by industries in the state.
⇨ Illegal mines also causes major problems to the surrounding environment and it is said that such mining activities destroy the environment, pollute the water and kill the fish etc.
⇨ National Green Tribunal had put a blanket ban on Coal mining Activities in Meghalya around four years ago. A step taken in a right spirit has unfortunately helped in the increase of the ill legal mining activities in Mehalaya. It is estimated that mining activities prior to this ban were giving the state a revenue of around 700 Crore.
⇨ Several activist opposing the idea of Rat Hole Mines have been severely injured allegedly by Mine Mafia in recent past.
The never ending ordeal of mine workers in picture
What are they saying about the tragedy ?
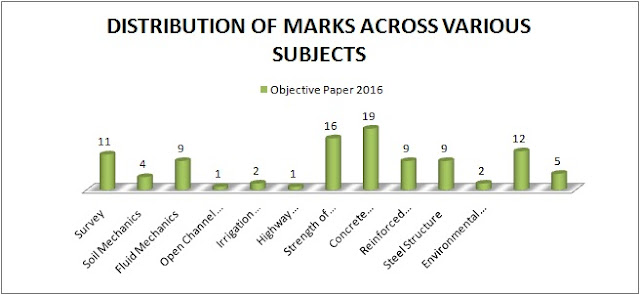
SSC JE MARKS DISTRIBUTION ACROSS VARIOUS SUBJECTS IN OBJECTIVE PAPER OF 2016
We would like to welcome all the visitors who are currently reading this. Efforts are once again being made to analyse the objective paper of SSC Junior Engineer Exam 2016. Same efforts was also made for the objective paper of SSC JE 2012 but after that such efforts were not made by the Admin Team due to the various constraints.
SSC JE 2017 is scheduled on 23 to 25 Dec 2017 and you all must be trying your level best to achieve the required cutoff percentage. For those, who have completed all the subjects already, it will be very easy to crack the exam. But still few peoples must be trying to cope up the time, which had been wasted by them. As we also belong to the second category of students, so we have an idea of their requirements. ☺
An analysis has been carried out by the Admin team for the objective paper of 2016. It is a well understood fact that pattern of paper remain more or less same so this type of marks distribution will help the students in prioritizing the subjects.
Hope it is going to help you to either begin from the scratch or improve your position if you are already in the race.
Please comment and share if enjoyed the post and content. Author will be highly indebted of your kind gesture.
SSC JE 2016 MARKS DISTRIBUTION ACROSS VARIOUS SUBJECTS IN OBJECTIVE PAPER.
S.No.
|
Subject
|
Marks
|
1
|
Survey
|
11
|
2
|
Soil
Mechanics
|
4
|
3
|
Fluid
Mechanics
|
9
|
4
|
Open
Channel Flow
|
1
|
5
|
Irrigation
Engineering
|
2
|
6
|
Highway
Engineering
|
1
|
7
|
Strength
of Material
|
16
|
8
|
Concrete
Technology
|
19
|
9
|
Reinforced
Cement Concrete
|
9
|
10
|
Steel
Structure
|
9
|
11
|
Environmental
Engineering
|
2
|
12
|
Building
Material & Construction
|
12
|
13
|
Estimation
& Costing
|
5
|
Few Points to Ponder :-
1. Survey :- Although majority of Questions asked were directly from Gupta and Gupta but one question was also asked from Transition curves. Made Easy Notes will help in this regard.
2. Soil Mechanics :- Only 04 Questions were asked from this subject. It seems that this evergreen subject is loosing its charm. But from practical aspects too, soil mechanics is not a very important subject for the jobs where you have to majorly deal with the construction activities. But still you must focus on this subject.
3. Fluid Mechanics :- One question was asked from pressure flow in pipes. Such question are bit harder side as far as Junior Engineer is concerned. Rest of the questions were easy in nature.
4. Open Channel Flow :- Only one question was asked from open channel flow and that too from Hydraulic Jump.
5. Irrigation Engineering : Only 2 questions. Gupta and Gupta Level.
6. Highway Engineering ;- One Question from Geometrical Design.
7. Concrete Technology. : Questions were easy but you need to remember them. Level Gupta and Gupta.
8. RCC :- Total 09 Questions. Majority of them were based directly on the provisions of IS 456 :2000. One question was also asked from prestress losses.
9. Steel Structure : 09 Questions from rivets.
10. Environment : 02 questions. That too from air pollution only.
11. Building Material : Easy questions. You need to remember them. Gupta and Gupta will suffice.
12. Estimation and Costing : Total 05 Question. One from Contract terminology. Rest were easy in nature. Gupta and Gupta will suffice.
As of now I am terminating the post here itself but will enhance it further in coming one or two days by including the analysis of Objective paper of 2014 and 2015.
Please feel free to suggest anything related to the post and also kindly promote the blog by sending the link to your dear ones.
THANK YOU
SEWAGE SYSTEM IN INDIA
A combination of sewer lines and manholes which helps to dispose the sludge away from the owner's property to either a septic tank or a public line is known as sewage system. In this post we will try to focus on some basic points related to sewage system. This post may not be useful for exam point of view, but we are sure that it will be beneficial for interview point of view Etc.
Some Basic points which a site Engineer or Contractor has to keep in mind while designing a sewage line are as follows :-
- The water pipes and sludge pipes entering or exiting a building should be on opposite face of a building. This will avoid the accidental interaction of fresh water and sludge. Moreover positioning of both the pipes on a same face of a building has some pshycological problems associated with it.
- The sewage line exiting from the owner's property should connect the main line at an angle of 60 Degree with the direction of the main line. It will avoid the back flowing of water up to some extent in case of blockage in Main public line.
- Intercepting Traps can also be provided at the Junction of Building sewer and Public Sewer. These intercepting Traps not only eliminate the possibility of foul smells but also check the entry of rodents in to the Building Sewer.
- Anti flood Valve can also be installed at such junction where back flowing of sludge from the Main public line to the Building sewer is a possibility.
A youtube video is also attached to look at the working of one such trap.
Hope this video has clarified the working of Intercepting Trap.
- After completion of work testing should be first completed before covering the laid sewer line with concrete or any other material.
- Manhole should be constructed at any change in the direction of sewage line or at the change of the gradient. In a straight sewer line Manhole should be kept at a proper spacing.
- Manhole dimension depends on the depth of the manhole. The dimension of manhole should increase with depth as with increasing depth it becomes difficult for the inspecting person to enter in to the manhole with small dimension.
- Drop Manhole should be constructed at locations where Highest level of sludge in public sewer and invert level of Building sewer has a difference in level of around 600 mm. Drop manholes are provided so that workers can easily operate at such location.
Testing of Sewer Line
We all have read about few tests which are conducted to locate the seepage in the sewage line. Here we are not going in to the theory part as we know that you all are aware about that. We are providing some video links which will help you to understand these tests in better practical way.
- Smoke Test
- Ball Test
Videos for the remaining test will also be updated once found.
This post will be updated regularly. So Plz feel free to ask anything specific related to this post.
Hope you enjoyed the post.
All thes Papers are based on the memory of the students who have qualified the exam previously.
Railway Recruitment Board
Senior Section Engineer and Junior Engineer Exam 2015
Railway Recruitment Board has invited application for the post of Senior Section Engineer and Junior Engineer.
The exam will be of General Engineering. Questions will be asked from the subjects like Thermodynamics, Principle of Electrical Engineering, Basic Mechanical Engineering and various other subjects taught during first few year of degree course.
One should not get any confusion regarding the exam pattern. Exam Pattern will remain same for all the post, for all the departments. It may happen that you are writing the exam for Junior Engineer Civil Post and you may only get 3 question from civil engineering in Paper.
By keeping in mind the trauma faced by students, we are hereby posting the previous year paper of RRB Senior section Engineer Exam and Junior Exam.
Needless to say that your comments and suggestions will be appreciated.
Glimpses of laboratory of Soil giant
Karl Terzaghi is known as father of soil Mechanics. His theories published long ago have covered the entire area of soil Mechanics and even after so many ears his theories have not lost their charm in field of Geotechnical Engineering.
Today we are conducting experiments on all those machines in our Geotechnical Laboratories. Technology is changing very fast and all the manual works are shifting to the automatic era. Gone are the days, when we had to manually produce the graphs at our sheet after conducting a experiments. With advancement in electronic technology, the automatic machines in laboratories are helping us in reducing the burden of conducting experiments.
Ever wonder, how those giants of soil Mechanics were conducting experiments in laboratories? While surfing on internet we found out some of the instruments used by Karl Terzaghi in laboratories.
The experimental findings of these set ups are so correct that they are relevant even today.
 |
| Triaxial Cell |
 |
| Direct Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Ring Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| Ring cell |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| New Direct Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| Triaxial Cell |
 |
| Triaxial cell |
 |
| Triaxial Cell |
 |
| Ring Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Ring Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Ring Shear Apparatus |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| Consolidometer |
 |
| Direct Shear |
 |
| Direct Shear |
 |
| Direct Shear |
 |
| Direct Shear |
 | ||||
| Direct Shear |
Feel free to suggest and comment!!!!!!
Tutorial Sheets and other related Practice Material
As promised, We have arranged some material to practice in various Civil Engineering Subjects.
Our focus here is to provide quality material to practice.
We are starting with Soil Mechanics as it is the most Important subject of Civil Engineering.
In Near Future we will add material related to some other subjects depending on the response to this post.
- Soil Mechanics
Kindly mention below in Comment section, the name of subject for which you need practice material.
We love your response and we will try level our best to provide the required material in a time bound manner
Join Us On Facebook
Soil Mechanics lab Experiment
During undergraduate studies we all face difficulties in conducting experiments. The reasons varies from faulty instruments to the lack of laboratory manuals.
In soil mechanics after the completion of basic experimental work like In-situ density or Proctor Test, the enthusiasm of a student comes to an end after seeing the scary set up of Unconfined compressive strength test apparatus or Consolidometer. One should not be afraid of these instruments as it had happened with every Civil Professional during his or her studies.
Usually the number of experiments in Universities all around India, are more or less same. While searching on youtube, we found some really beautiful videos, explaining in details the soil Mechanics Laboratory Experiments.
We hope that these videos will be beneficial for all the undergraduate students who want to learn the soil mechanics experiments.
- Unconfined Compressive Strength Test.
- Direct Shear Test
- Core Cutter Method
- Sand Replacement Method
- Specific Gravity of Soil
- Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregates
- Liquid Limit determination by Cone Penetrometer
- Determination of Liquid Limit and Plastic Limit
- Standard Penetration Test
- Soil Sampling
- Water Content Determination
We are trying our level best to bring some more relevant experimental videos.
In case we missed some crucial experiments of soil mechanics, remind us by commenting below.
If you have some video link, which in your opinion should be included here, kindly post the link below as a comment or send the link to us via Contact Us .
Feel free to suggest anything.
UPSC MAINS CIVIL ENGINEERING SYLLABUS
Paper-I
1. Engineering Mechanics, Strength of Materials and Structural Analysis:1.1 Engineering Mechanics:
Units and Dimensions, SI Units, Vectors, Concept of Force, Concept of particle and rigid body. Concurrent, Non Concurrent and parallel forces in a plane, moment of force, free body diagram, conditions of equilibrium, Principle of virtual work, equivalent force system.
First and Second Moment of area, Mass moment of Inertia.
Static Friction.
Kinematics and Kinetics:
Kinematics in Cartesian Co-ordinates, motion under uniform and nonuniform acceleration, motion under gravity. Kinetics of particle: Momentum and Energy principles, collision of elastic bodies, rotation of rigid bodies.
1.2 Strength of Materials:
Simple Stress and Strain, Elastic constants, axially loaded compression members, Shear force and bending moment, theory of simple bending, Shear Stress distribution across cross sections, Beams of uniform strength.
Deflection of beams: Macaulay's method, Mohr's Moment area method, Conjugate beam method, unit load method. Torsion of Shafts, Elastic stability of columns, Euler's Rankine's and Secant formulae.
1.3 Structural Analysis:
Castiglianio's theorems I and II, unit load method of consistent deformation applied to beams and pin jointed trusses. Slope-deflection, moment distribution,
Rolling loads and Influences lines: Influences lines for Shear Force and Bending moment at a section of beam. Criteria for maximum shear force and bending Moment in beams traversed by a system of moving loads. Influences lines for simply supported plane pin jointed trusses.
Arches: Three hinged, two hinged and fixed arches, rib shortening and temperature effects.
Matrix methods of analysis: Force method and displacement method of analysis of indeterminate beams and rigid frames.
Plastic Analysis of beams and frames: Theory of plastic bending, plastic analysis, statical method, Mechanism method.
Unsymmetrical bending: Moment of inertia, product of inertia, position of Neutral Axis and Principle axes, calculation of bending stresses.
2. Design of Structures: Steel, Concrete and Masonry Structures:
2.1 Structural Steel Design:
Structural Steel: Factors of safety and load factors. Riveted, bolted and welded joints and connections. Design of tension and compression member, beams of built up section, riveted and welded plate girders, gantry girders, stancheons with battens and lacings.
2.2 Design of Concrete and Masonry Structures:
Concept of mix design. Reinforced Concrete: Working Stress and Limit State method of design–Recommendations of I.S. codes Design of one way and two way slabs, stair-case slabs, simple and continuous beams of rectangular, T and L sections. Compression members under direct load with or without eccentricity,
Cantilever and Counter fort type retaining walls.
Water tanks: Design requirements for Rectangular and circular tanks resting on ground.
Prestressed concrete: Methods and systems of prestressing, anchorages, Analysis and design of sections for flexure based on working stress, loss of prestress.
Design of brick masonry as per I.S. Codes
3. Fluid Mechanics, Open Channel Flow and Hydraulic Machines:
3.1 Fluid Mechanics:
Fluid properties and their role in fluid motion, fluid statics including forces acting on plane and curved surfaces.
Kinematics and Dynamics of Fluid flow: Velocity and accelerations, stream lines, equation of continuity, irrotational and rotational flow, velocity potential and stream functions.
Continuity, momentum and energy equation, Navier-Stokes equation, Euler's equation of motion, application to fluid flow problems, pipe flow, sluice gates, weirs.
3.2 Dimensional Analysis and Similitude:
Buckingham's Pi-theorem, dimensionless parameters.
3.3 Laminar Flow:
Laminar flow between parallel, stationary and moving plates, flow through tube.
3.4 Boundary layer: Laminar and turbulent boundary layer on a flat plate, laminar sub layer, smooth and rough boundaries, drag and lift. Turbulent flow through pipes: Characteristics of turbulent flow, velocity distribution and variation of pipe friction factor, hydraulic grade line and total energy line.
3.5 Open channel flow:
Uniform and non-uniform flows, momentum and energy correction factors, specific energy and specific force, critical depth, rapidly varied flow, hydraulic jump, gradually varied flow, classification of surface profiles, control section, step method of integration of varied flow equation.
3.6 Hydraulic Machines and Hydropower:
Hydraulic turbines, types classification, Choice of turbines, performance parameters, controls, characteristics, specific speed. Principles of hydropower development.
4. Geotechnical Engineering:
Soil Type and structure – gradation and particle size distribution – consistency limits.
Water in soil – capillary and structural – effective stress and pore water pressure – permeability concept – field and laboratory determination of permeability – Seepage pressure – quick sand conditions – Shear strength determination – Mohr Coulomb concept.
Compaction of soil – Laboratory and field tests.
Compressibility and consolidation concept – consolidation theory – consolidation settlement analysis.
Earth pressure theory and analysis for retaining walls, Application for sheet piles and Braced excavation.
Bearing capacity of soil – approaches for analysis – Field tests – settlement analysis – stability of slope of earth walk.
Subsurface exploration of soils – methods
Foundation – Type and selection criteria for foundation of structures – Design criteria for foundation – Analysis of distribution of stress for footings and pile – pile group action-pile load test. Ground improvement techniques.
Paper-II
1. Construction Technology, Equipment, Planning and Management:1.1 Construction Technology:
Engineering Materials:
Physical properties of construction materials with respect to their use in construction - Stones, Bricks and Tiles; Lime, Cement, different types of Mortars and Concrete.
Specific use of ferro cement, fibre reinforced C.C, High strength concrete.
Timber, properties and defects - common preservation treatments.
Use and selection of materials for specific use like Low Cost Housing, Mass Housing, High Rise Buildings.
1.2 Construction:
Masonry principles using Brick, stone, Blocks – construction detailing and strength characteristics.
Types of plastering, pointing, flooring, roofing and construction features.
Common repairs in buildings.
Principles of functional planning of building for residents and specific use - Building code provisions.
Basic principles of detailed and approximate estimating - specification writing and rate analysis – principles of valuation of real property.
Machinery for earthwork, concreting and their specific uses – Factors affecting selection of equipments – operating cost of Equipments.
1.3 Construction Planning and Management:
Construction activity – schedules- organization for construction industry – Quality assurance principles.
Use of Basic principles of network – analysis in form of CPM and PERT – their use in construction monitoring, Cost optimization and resource allocation.
Basic principles of Economic analysis and methods.
Project profitability – Basic principles of Boot approach to financial planning – simple toll fixation criterions.
2. Surveying and Transportation Engineering
2.1 Surveying:
Common methods and instruments for distance and angle measurement for CE work – their use in plane table, traverse survey, leveling work, triangulation, contouring and topographical map.
Basic principles of photogrammetry and remote sensing.
2.2 Railway Engineering:
Permanent way – components, types and their functions – Functions and Design constituents of turn and crossings – Necessity of geometric design of track – Design of station and yards.
2.3 Highway Engineering:
Principles of Highway alignments – classification and geometrical design elements and standards for Roads.
Pavement structure for flexible and rigid pavements - Design principles and methodology of pavements.
Typical construction methods and standards of materials for stabilized soil, WBM, Bituminous works and CC roads.
Surface and sub-surface drainage arrangements for roads - culvert structures.
Pavement distresses and strengthening by overlays.
Traffic surveys and their applications in traffic planning - Typical design features for channelized, intersection, rotary etc – signal designs – standard Traffic signs and markings.
3. Hydrology, Water Resources and Engineering:
3.1 Hydrology:
Hydrological cycle, precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, infiltration, overland flow, hydrograph, flood frequency analysis, flood routing through a reservoir, channel flow routing-Muskingam method.
3.2 Ground water flow:
Specific yield, storage coefficient, coefficient of permeability, confined and unconfined equifers, aquifers, aquitards, radial flow into a well under confined and unconfined conditions.
3.3 Water Resources Engineering:
Ground and surface water resource, single and multipurpose projects, storage capacity of reservoirs, reservoir losses, reservoir sedimentation.
3.4 Irrigation Engineering:
(i) Water requirements of crops: consumptive use, duty and delta, irrigation methods and their efficiencies.
(ii) Canals: Distribution systems for canal irrigation, canal capacity, canal losses, alignment of main and distributory canals, most efficient section, lined canals, their design, regime theory, critical shear stress, bed load.
(iii) Water logging: causes and control, salinity.
(iv) Canal structures: Design of, head regulators, canal falls, aqueducts, metering flumes and canal outlets.
(v) Diversion headwork: Principles and design of weirs of permeable and impermeable foundation, Khosla's theory, energy dissipation.
(vi) Storage works: Types of dams, design, principles of rigid gravity, stability analysis.
(vii) Spillways: Spillway types, energy dissipation.
(viii) River training: Objectives of river training, methods of river training.
4. Environmental Engineering:
4.1 Water Supply:
Predicting demand for water, impurities, of water and their significance, physical, chemical and bacteriological analysis, waterborne diseases, standards for potable water.
4.2 Intake of water:
Water treatment: principles of coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation; slow-; rapid-, pressure-, filters; chlorination, softening, removal of taste, odour and salinity.
4.3 Sewerage systems:
Domestic and industrial wastes, storm sewage–separate and combined systems, flow through sewers, design of sewers.
4.4 Sewage characterization:
BOD, COD, solids, dissolved oxygen, nitrogen and TOC. Standards of disposal in normal watercourse and on land.
4.5 Sewage treatment:
Working principles, units, chambers, sedimentation tanks, trickling filters, oxidation ponds, activated sludge process, septic tank, disposal of sludge, recycling of wastewater.
4.6 Solid waste: Collection and disposal in rural and urban contexts, management of long-term ill effects.
5. Environmental pollution: Sustainable development. Rawastes and disposal. Environmental impact assessment for thermal power plants, mines, river valley projects. Air pollution. Pollution control acts
Click Here to Download UPSC Mains Previous Year Paper of Civil Engineering