Problems Dated Nov 05 2021.
To read More Such Posts related to Class 10 Click on the Links Given Below :-
Exercise 3E R S Agarwal
Problem No 01
Chair = x
Tables = y
5 x + 4 y = 5600 ..... 1
4 x + 3 y = 4340 ....... 2
1 * 4 & 2 * 5
20x + 16 y = 22400.......... a
20x + 15y = 21700............b
a-b
y = 700
5x + 2800 = 5600
5x = 2800
x = 560 Ans
Problem No 02
To read More Such Posts related to Class 10 Click on the Links Given Below :-
MISC
Maths Problems dated 03 Nov 2021
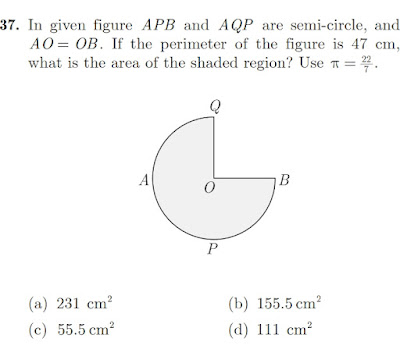
Area of Shaded Region
To read More Such Posts related to Class 10 Click on the Links Given Below :-
Chapter 02 Polynomials
Problem No 01 :- Find the Zeros of the Polynomials and verify the relationship between the zeros and coefficients :-
x2 + 7x + 12
To find the zeros of polynomial, It should be equated to zero first
Hence,
x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
Or, x2 + 4x + 3x + 12 = 0
Or, x (x + 4)+ 3 (x + 4 ) = 0
Or, (x + 3) * (x + 4 ) = 0
It implies that x = - 3 & -4 Ans ............................................... (1)
Comparing the Given Eqn with Stnd Eqn i.e. ax2 + bx + c = 0
We Get, a=1 , b = 7 & c = 12
α + β = -3 + ( - 4) = - 7................................... (2)
-b /a = -7 / 1 = -7 .............................................(3)
Also α * β = -3 * -4 = 12 .................................(4)
c / a = 12 / 1 ......................................................(5)
From (2), (3) (4) & (5) relation between the zeros and coefficients can be verified.
CLASS 10 MATHEMATICS
- Real Numbers
- Polynomials
- Linear Equation in Two Variables
- Triangles
- Trigonometric Ratios.
- T-Ratios of some Particular Angles.
- Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles.
- Trigonometric Identities.
- Mean, Median, Mode of Grouped Data, Cumulative Frequency Graph and Ogive.
- Quadratic Equations
- Arithmetic Progressions.
- Constructions
- Circles
- Heights and Distances
- Probability
- Coordinate Geometry
- Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures.
- Area of Circle, Sector and Segment
- Volume and Surface Area of Solids
- Misc Problems
To read More Such Posts related to Class 10 Click on the Links Given Below :-
Class 10 Area

As per the Diagram
EC = BC (Radius in Sector BGEC)
Hence EC = 7 Cm.
DE = 4 cm Given
DC = DC + EC
= 4 CM + 7 CM = 11 cm
Area of trapezium ABCD
= (1/2) *( Sum Of ||el sides) * (Height)
= (1/2) * (AB+DC) *(BF)
=(1/2) * (7 cm + 11 cm ) * (3.5 cm )
= 0.5 * 18 cm * 3.5 cm
= 9 cm * 3.5 cm
= 31.50 cm2
Area of Sector BGEC :-
(O/360) *( pi *r*r)
= (30/360) *(22/7*7*7)
(1/12) * (22*7)
= 12.83 cm2
Area Of shaded portion = Area of trapezium - Area of Sector
= 31.50 cm2 - 12.83 cm2
= 18.67 cm2
Hence the Right answer is (d).
Please like share and comment.
Do write us for any other numerical related to Class 10 Mathematics.
Thank you.
To read More Such Posts related to Class 10 Click on the Links Given Below :-
Plumbing
Plumbing notes based on SP-35 1987 are as follows :-
1. General
- Plumbing System includes
- water supply and distributing pipes
- plumbing fixtures for the use in water supply
- sanitary drainage system to carry the wastes
- Anti-siphonage system which carry only the air for the purpose of ventilation
- Storm water drainage system to collect and carry rain water
- Planning for Plumbing
- The layout of the building should be such as to allow for good and economical plumbing to be carried out.
- Cross connection between water supply and waste water pipes should be avoided.
- Noise associated with Plumbing system (Water Pumps) should be kept in mind.
- When a water pipe is to be concealed, it must be wrapped with Hassian cloth dipped in bitumen. Hassian Cloth can be seen in the picture given below :-
-
- Single Pipe system is now generally preferred over two pipe systems.
- Indian Standards should be adopted while selecting materials, equipment, construction or testing the fixtures so that uniformity can be maintained.
Principles of Plumbing.
- Plumbing Fixtures should be smooth and non absorbent, well ventilated, away from fouling places, easily accessible, leak free.
- Plumbing system should help in using the water economically, should avoid cross connection of water and sewerage line, well ventilated and well designed.
Thank you.
Further Read in this Series :-
Principle of Effective Stress, Capillarity and Permeability
Numerical
NUMERICAL ON SOIL CLASSIFICATION
1. Numerical of Gopal Ranjan and AS RAO Book.
Given Details as shown below in the numerical. We need to classify the soil as per indian Standard.
| Sieve Size (mm) | Percent Finer | ||
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | |
| 4.75 | 100.00 | 1001 | 100 |
| 2 | 100.00 | 99.25 | 100 |
| 1 | 99.80 | 98.75 | 99.9 |
| 0.45 | 99.65 | 98 | 99.7 |
| 0.212 | 98.95 | 54.15 | 90 |
| 0.15 | 97.55 | 7.6 | 81.5 |
| 0.075 | 96.85 | 6 | 63 |
| wL | 23.00 | '---- | '--- |
| wp | 16.77 | '---- | '--- |
| IP | 6.23 | Non Plastic | Non Plastic |
Grain Size Curve is as Follows :-